ATSL 냉각팬 개발 공정 계획(1)
- Strategy for Market Leadership:
- Purpose: Establish a strategy to release a competitive product that can dominate the market.
- Key Activities: Market research is conducted to select the target market and identify differentiating factors compared to competitor products. For example, features like low noise, high cooling performance, and low power consumption can be emphasized.
- Outcome: The product’s key competitive points are defined, guiding the direction for marketing and product development.
- Development Specification:
- Purpose: Define detailed product specifications to set the foundation for design and development.
- Key Activities: Specifications such as fan speed (RPM), size, noise level (dB), airflow (CFM), power consumption (W), and operating temperature range are detailed.
- Outcome: A comprehensive specification document is completed, serving as a guideline for the development process.
- Construction:
- Purpose: Design the basic mechanical structure of the fan.
- Key Activities: Aerodynamic design is crucial, deciding the shape, size, and angle of the fan blades. Since the structure of the blades directly affects airflow and cooling performance, precise design is required.
- Outcome: A design is completed using 3D modeling software, which will be used in the next stages of simulation and prototyping.
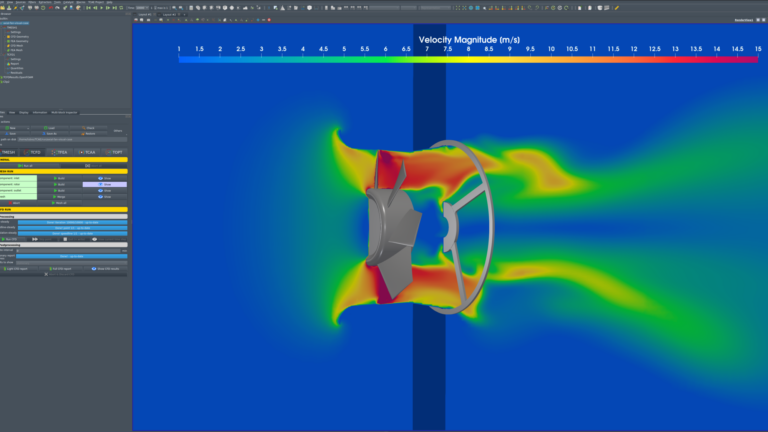
- Simulation:
- Purpose: Virtually assess the performance before actual production to optimize the design.
- Key Activities: CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) simulations are conducted to analyze airflow, cooling performance, and noise levels. Various fan blade designs and motor combinations are simulated to find the best performance.
- Outcome: The design is validated in a virtual environment, ensuring the performance is guaranteed by the structure.
- Prototyping (3D Printing/CNC Milling):
- Purpose: Create a full-scale fan model for physical testing.
- Key Activities: 3D printing is used to create fan blades and structures, or CNC milling is used for high-precision parts. These prototypes are tested for design verification and assembly.
- Outcome: A physical prototype is completed and enters the testing phase.
- EVT (Engineering Validation Test: Performance, Acoustics, Compatibility):
- Purpose: Validate the main performance indicators of the product.
- Key Activities: The fan’s performance (cooling efficiency, airflow), noise level, and compatibility with various PC cases and devices are evaluated.
- Outcome: EVT results confirm the product’s performance and acoustics, and necessary design modifications are identified.
- TCE (Thermal Creep Evaluation):
- Purpose: Evaluate how the fan materials and components withstand long-term exposure to high temperatures.
- Key Activities: The thermal creep characteristics of the fan are assessed under various temperature conditions to ensure durability and performance retention at high temperatures.
- Outcome: The material and design are validated for heat resistance, and adjustments are made if necessary.
- DFM (Design for Manufacturing) Validation:
- Purpose: Ensure the design is suitable for mass production and optimize manufacturing efficiency.
- Key Activities: Potential issues in the production process are analyzed, and design modifications are made to solve them. Simplification and standardization of parts are considered to streamline the manufacturing process.
- Outcome: The design is optimized for production, and the product is ready for mass production.
- Motor Design:
- Purpose: Design the motor, which significantly impacts the fan’s performance.
- Key Activities: The motor is designed to optimize fan speed, torque, and power consumption. It’s important to focus on a quiet and efficient motor that contributes to the fan’s overall performance.
- Outcome: The motor specifications are finalized, and optimization with the fan is completed.
- Material Selection:
- Purpose: Select appropriate materials that ensure performance and durability.
- Key Activities: Materials for components such as the fan blades and casing are chosen, considering factors like weight, thermal resistance, noise absorption, and cost.
- Outcome: Material specifications are finalized, and components are produced based on these materials.
- Injection Mold Construction:
- Purpose: Design and construct molds for mass production.
- Key Activities: Molds for forming the parts are designed and constructed, ensuring consistent, high-quality production of the components.
- Outcome: Molds are completed, and mass production is ready to begin.
- Injection Mold Manufacturing:
- Purpose: Manufacture components in large quantities using the injection mold.
- Key Activities: Injection molding machines are used to mass-produce the fan’s components. In this process, production speed and quality control are critical.
- Outcome: Consistent, high-quality components are produced in large quantities.
- Determining Injection Molding Parameters:
- Purpose: Set parameters for injection molding to ensure optimal production efficiency and quality.
- Key Activities: Variables such as temperature, pressure, and cooling time are optimized to maximize product quality and production efficiency.
- Outcome: Products are manufactured with quality assurance using optimized production parameters.
- Prototype Production:
- Purpose: Produce small batches of the final design to verify real-world performance.
- Key Activities: A small quantity of prototypes is produced on the production line, and performance tests are conducted in real-world conditions.
- Outcome: The performance and manufacturability of the final product are confirmed.
- DVT (Design Validation Testing):
- Purpose: Perform final validation to ensure the design meets all specifications.
- Key Activities: Cooling performance, noise, power consumption, and durability are re-tested to confirm that the design is complete and ready for mass production.
- Outcome: The product matches the final design and is confirmed for large-scale production.
- Fine-tuning of Molding Tool/Parameters:
- Purpose: Resolve any minor issues in the manufacturing process and ensure flawless quality.
- Key Activities: Fine-tuning of the molding tools and injection molding parameters is carried out to finalize product quality.
- Outcome: The production process is optimized, ensuring high-quality products.
- Small-scale Production Run:
- Purpose: Conduct a small production run before full-scale production to ensure stability in the production process.
- Key Activities: Small-scale production is used to identify any remaining issues in the process, making final preparations for mass production.
- Outcome: The small-scale production results are used to make the final adjustments for mass production.
- MVT (Manufacturing Validation Tests):
- Purpose: Validate that the mass production process meets all quality standards.
- Key Activities: The production line produces the product in large quantities, evaluating and solving any potential issues during production.
- Outcome: All tests are completed, and the product is ready for mass production.
- MVT Preparation:
- Purpose: Complete all preparations for the manufacturing validation tests (MVT).
- Key Activities: The production line is inspected, and necessary tools and equipment are prepared to carry out MVT smoothly.
- Outcome: All preparations are completed, and MVT can proceed.
- MVT Procedure:
- Purpose: Execute the procedures for MVT.
- Key Activities: The MVT procedure is followed to review performance, quality, and efficiency during large-scale production, with any necessary adjustments made.
- Outcome: The manufacturing process is optimized, and mass production can begin.
- LTCV (Long-term Thermal Creep Validation):
- Purpose: Evaluate the fan’s ability to withstand prolonged exposure to heat without deformation or performance degradation.
- Key Activities: The fan is tested over a long period at high temperatures to ensure no performance loss due to thermal creep.
- Outcome: The fan is confirmed to maintain performance over long-term use.
- MVT Evaluation & Analysis:
- Purpose: Analyze the results of the MVT and evaluate the readiness for mass production.
- Key Activities: The MVT results are analyzed, and any issues in the production process are resolved to ensure flawless mass production.
- Outcome: All tests are completed, and the product is ready for large-scale production.
- 마켓 리더십 전략 (Strategy for Market Leadership):
- 목적: 경쟁력 있는 제품을 시장에 내놓기 위한 전략을 수립하는 단계이다.
- 주요 활동: 시장 조사를 통해 타겟 시장을 선정하고, 경쟁 제품과의 차별화 요소를 결정한다. 예를 들어, 저소음 팬, 고성능 냉각 시스템, 저전력 소비 등의 특징이 강조될 수 있다.
- 결과: 제품의 주요 경쟁력 포인트가 정의되고, 이를 통해 마케팅 및 제품 개발 방향이 결정된다.
- 개발 사양 (Development Specification):
- 목적: 제품의 세부 사양을 정의하여 설계 및 개발의 기준을 설정한다.
- 주요 활동: 팬 속도(RPM), 크기, 소음 수준(dB), 공기 흐름(CFM), 전력 소비량(W), 사용 환경 온도 등의 기술 사양을 정리한다.
- 결과: 상세한 사양 문서가 완성되고, 이는 개발 과정의 지침이 된다.
- 구조 설계 (Construction):
- 목적: 팬의 기본적인 기계 구조를 설계하는 단계이다.
- 주요 활동: 공기역학적인 설계가 중요하며, 팬 블레이드의 모양, 크기, 각도를 결정한다. 블레이드의 구조가 공기 흐름과 냉각 성능에 직접적인 영향을 미치므로 정교한 설계가 필요하다.
- 결과: 3D 모델링 소프트웨어를 사용해 설계도가 완성되고, 이는 이후 시뮬레이션 및 프로토타입 제작에 활용된다.
- 시뮬레이션 (Simulation):
- 목적: 실제 제작 전에 가상으로 성능을 평가하여 설계의 최적화를 이끌어낸다.
- 주요 활동: CFD(Computational Fluid Dynamics)를 사용해 공기 흐름, 냉각 성능, 소음을 분석한다. 다양한 팬 블레이드 설계와 모터 조합을 시뮬레이션해 최적의 성능을 찾는다.
- 결과: 설계가 가상 환경에서 평가되어 성능이 보장된 구조로 검증된다.
- 프로토타이핑 (3D 프린팅/CNC 밀링):
- 목적: 실물 크기의 팬 모델을 제작하여 실제 물리적 테스트를 진행한다.
- 주요 활동: 3D 프린터를 사용해 팬 블레이드 및 구조물을 제작하거나 CNC 밀링을 통해 고정밀 부품을 생산한다. 이를 통해 설계 검증 및 조립성 테스트를 진행한다.
- 결과: 실제 프로토타입이 완성되어 테스트에 들어간다.
- EVT (엔지니어링 검증 테스트: 성능, 소음, 호환성):
- 목적: 제품의 주요 성능 지표를 검증하는 단계이다.
- 주요 활동: 팬의 성능(냉각 효율, 공기 흐름), 소음 수준, 다양한 PC 케이스 및 장치와의 호환성을 평가한다.
- 결과: EVT 결과를 바탕으로 성능과 소음 측면에서 제품의 초안을 검증하며, 필요한 설계 수정 사항을 도출한다.
- TCE (열 크리프 평가):
- 목적: 팬이 장시간 높은 열에 노출되었을 때 재료의 변형이나 성능 저하 여부를 확인한다.
- 주요 활동: 다양한 온도 조건에서 팬의 열 크리프 특성을 평가하여, 고온에서의 내구성과 성능 유지를 보장한다.
- 결과: 열에 강한 재료 및 설계가 검증되며, 필요시 재료 변경이나 설계 보완이 이루어진다.
- DFM (제조를 위한 설계) 검증:
- 목적: 대량 생산이 가능한지 확인하고, 제조 효율성을 높이기 위한 설계 최적화를 진행한다.
- 주요 활동: 제품의 제조 공정에서 발생할 수 있는 문제를 미리 분석하고, 이를 해결하기 위한 설계 수정을 진행한다. 부품의 간소화, 표준화 등을 고려하여 제조 공정을 최적화한다.
- 결과: 설계가 생산 공정에 적합하게 수정되어 대량 생산 준비가 완료된다.
- 모터 설계 (Motor Design):
- 목적: 팬의 성능을 결정짓는 모터를 설계하는 단계이다.
- 주요 활동: 팬의 속도, 토크, 전력 소비 등을 최적화하기 위해 모터 사양을 설계한다. 저소음 모터, 고효율 모터가 중요하며, 팬의 전체 성능에 큰 영향을 미친다.
- 결과: 적절한 모터 사양이 결정되고, 팬과의 최적화가 완료된다.
- 재료 선택 (Material Selection):
- 목적: 성능과 내구성을 보장할 수 있는 적절한 재료를 선정한다.
- 주요 활동: 팬 블레이드, 팬 하우징 등 각 구성 요소에 사용할 재료를 선정한다. 무게, 열 저항성, 소음 흡수 성능, 비용 등을 고려하여 재료를 선택한다.
- 결과: 재료 사양이 최종적으로 결정되고, 이를 바탕으로 부품이 생산된다.
- 사출 금형 제작 (Injection Mold Construction):
- 목적: 대량 생산을 위한 금형을 설계하고 제작한다.
- 주요 활동: 각 부품을 성형하기 위한 금형을 설계하고, 이를 통해 고품질의 제품을 일관되게 생산할 수 있도록 준비한다.
- 결과: 금형이 완성되어 대량 생산 준비가 완료된다.
- 사출 성형 제조 (Injection Mold Manufacturing):
- 목적: 금형을 사용하여 부품을 대량으로 생산하는 단계이다.
- 주요 활동: 사출 성형기를 이용해 팬의 각 부품을 대량 생산한다. 이 과정에서 생산 속도와 품질 관리가 중요하다.
- 결과: 대량으로 일관성 있는 부품이 생산된다.
- 사출 성형 매개변수 결정 (Determining Injection Moulding Parameters):
- 목적: 최적의 생산 효율성과 품질을 보장하기 위한 사출 성형 매개변수를 설정한다.
- 주요 활동: 사출 성형 시 사용될 온도, 압력, 냉각 시간 등의 변수를 최적화하여, 제품의 품질과 생산성을 극대화한다.
- 결과: 최적화된 생산 매개변수로 품질이 보장된 제품이 생산된다.
- 프로토타입 생산 (Prototype Production):
- 목적: 최종 설계가 반영된 프로토타입을 소량 생산하여 실제 성능을 확인한다.
- 주요 활동: 생산 라인에서 소량의 프로토타입을 생산하고, 이를 바탕으로 실제 사용 환경에서 성능을 테스트한다.
- 결과: 최종 제품의 성능과 제조 공정이 적합한지 확인된다.
- DVT (설계 검증 테스트):
- 목적: 설계가 모든 사양을 충족하는지 최종적으로 검증한다.
- 주요 활동: 팬의 냉각 성능, 소음, 전력 소모, 내구성 등을 다시 한번 검증하여 설계가 문제없이 완성되었는지 확인한다.
- 결과: 제품이 최종 설계와 일치하며, 대량 생산이 가능한지 최종 확인된다.
- 금형 도구/매개변수 미세 조정 (Fine-tuning of Moulding Tool/Parameters):
- 목적: 제조 과정에서 발생할 수 있는 미세한 문제를 해결하고, 완벽한 품질을 보장한다.
- 주요 활동: 금형 도구의 미세 조정이나 사출 성형 매개변수의 세부 조정을 통해 제품의 품질을 최종적으로 완성한다.
- 결과: 생산 공정이 최적화되어 고품질 제품 생산이 보장된다.
- 소규모 생산 (Small-scale Production Run):
- 목적: 대량 생산 전에 소규모로 시험 생산을 진행하여 생산 공정의 안정성을 확인한다.
- 주요 활동: 소규모 생산을 통해 공정에서 발생할 수 있는 문제를 확인하고, 대량 생산 준비를 마친다.
- 결과: 소규모 생산 결과를 바탕으로 대량 생산을 위한 최종 수정이 이루어진다.
- MVT (제조 검증 테스트):
- 목적: 대량 생산 공정이 모든 품질 기준을 충족하는지 검증한다.
- 주요 활동: 생산 라인에서 제품을 대량으로 생산하며, 이 과정에서 발생할 수 있는 모든 문제를 평가하고 수정한다.
- 결과: 대량 생산에 필요한 모든 테스트가 완료되고, 생산 준비가 완료된다.
- MVT 준비 (MVT Preparation):
- 목적: 제조 검증 테스트를 위한 모든 준비를 완료한다.
- 주요 활동: 제조 라인을 점검하고 필요한 장비와 도구를 준비하여 MVT를 원활히 수행할 수 있도록 만반의 준비를 한다.
- 결과: 모든 준비가 완료되어 MVT를 수행할 수 있다.
- MVT 절차 (MVT Procedure):
- 목적: MVT 단계에서 수행해야 할 절차를 구체적으로 실행한다.
- 주요 활동: MVT 절차에 따라 대량 생산 과정에서의 성능, 품질, 효율성을 검토하며, 필요한 수정 작업을 진행한다.
- 결과: 제조 공정이 최적화되어 생산 준비가 완료된다.
- LTCV (장기 열 크리프 검증):
- 목적: 팬이 장기간 사용될 때 발생할 수 있는 열로 인한 변형이나 성능 저하를 평가한다.
- 주요 활동: 팬을 오랜 시간 동안 고온에서 테스트하여 열에 의해 성능이 저하되지 않는지 확인한다.
- 결과: 장기간 사용 시에도 성능이 유지되는 것이 확인된다.
- MVT 평가 및 분석 (MVT Evaluation & Analysis):
- 목적: MVT 결과를 분석하여 대량 생산 준비 상태를 최종 평가한다.
- 주요 활동: MVT 결과를 분석하고, 제조 공정에서 발생할 수 있는 문제를 해결하여 완벽한 대량 생산이 가능하도록 준비한다.
- 결과: 모든 테스트가 완료되고, 대량 생산 단계로 넘어갈 준비가 완료된다.
개선된 ATSL 냉각팬 개발 공정 계획
추가적 제안 및 개선 가능성
기존의 공정을 보다 직관적으로 정리하고, 연계성을 강화하여 설계, 검증, 제조 과정이 보다 체계적으로 진행될 수 있도록 구성할 수 있을 것이다.
- 공정 순서 조정 및 통합 제안
- 모터 설계(9번)와 재료 선택(10번)의 조기 수행: 팬 블레이드 및 구조 설계(3번)와 연계되어야 하는 중요한 요소이므로, 이 단계를 좀 더 앞당기는 것이 설계 최적화에 도움이 될 수 있다.
- TCE(7번)와 LTCV(21번)의 조화: 열 크리프 평가(TCE)와 장기 열 크리프 검증(LTCV)는 연계성이 높으므로, LTCV를 설계 검증(DVT, 15번) 이전에 위치시켜 장기적 신뢰성을 먼저 확보하는 것이 좋을 수 있다.
- 사출 성형 관련 공정(11~13번)의 통합: 금형 제작(11번)과 사출 성형 제조(12번), 성형 매개변수 결정(13번)을 하나의 단일 프로세스로 묶어 “금형 개발 및 생산 최적화” 단계로 정리하는 것도 가능해 보입니다.
- 추가 고려할 요소
- FEM(유한 요소 해석) 추가: 팬 블레이드의 구조적 강도 분석을 위해 FEM 해석을 시뮬레이션(4번) 과정에 추가하면 좋습니다. 이를 통해 고속 회전 중 변형이나 진동 문제를 사전에 방지할 수 있다.
- AI 및 머신러닝 적용: CFD 및 소음 최적화 과정에서 AI 기반 설계 최적화 기법을 적용하면 더 빠르고 정밀한 결과를 얻을 수 있다.
- 환경 영향 및 지속 가능성 평가: 친환경 소재 선택, 에너지 절감 설계 등을 위한 평가 과정이 추가되면 ESG(환경·사회·거버넌스) 관점에서도 경쟁력이 높아질 수 있다.
다음은 개정된 PC 팬 개발 공정이다. 기존의 공정을 보다 직관적으로 정리하고, 연계성을 강화하여 설계, 검증, 제조 과정이 보다 체계적으로 진행될 수 있도록 구성하였다.
- 시장 전략 수립 (Strategy for Market Leadership)
- 목적: 경쟁력 있는 제품을 시장에 내놓기 위한 전략을 수립
- 주요 활동:
- 시장 조사 및 타겟 시장 선정
- 경쟁 제품 분석 및 차별화 요소 결정 (예: 저소음, 고성능, 저전력 등)
- 결과: 제품의 주요 경쟁력 포인트 및 개발 방향 확립
- 개발 사양 정의 (Development Specification)
- 목적: 제품의 기술 사양을 명확히 정의
- 주요 활동:
- 팬 속도(RPM), 크기, 소음 수준(dB), 공기 흐름(CFM), 전력 소비량(W) 등의 명세 작성
- 사용 환경 및 내구성 기준 설정
- 결과: 제품 사양 문서 완성 (개발 기준 확립)
- 팬 구조 및 블레이드 설계 (Blade & Structural Design)
- 목적: 공기역학적으로 최적화된 팬 블레이드 및 구조 설계
- 주요 활동:
- 블레이드 형상, 크기, 각도 설계
- 구조적 강도 및 공기 흐름 최적화
- 3D 모델링 및 설계도 제작
- 결과: 설계 파일 및 시뮬레이션을 위한 기초 설계 완료
- 모터 설계 (Motor Design)
- 목적: 팬의 속도, 토크, 전력 소비를 고려한 최적의 모터 설계
- 주요 활동:
- 고효율, 저소음 모터 설계
- 팬과 모터 간 최적 조합 연구
- 결과: 적절한 모터 사양 결정 및 설계 확정
- 재료 선택 (Material Selection)
- 목적: 성능과 내구성을 보장할 수 있는 적절한 재료 선정
- 주요 활동:
- 블레이드 및 하우징의 소재 선택 (예: ABS, PBT, 카본 복합재 등)
- 내열성, 무게, 비용 등을 고려한 최적 재료 조합 결정
- 결과: 제품 제작을 위한 재료 확정
- CFD 및 FEM 해석 (CFD & FEM Analysis)
- 목적: 공기역학 성능과 구조 강도를 분석하여 최적화
- 주요 활동:
- CFD(Computational Fluid Dynamics) 분석을 통해 공기 흐름, 냉각 성능, 소음 평가
- FEM(Finite Element Method) 해석을 통해 고속 회전 시 블레이드의 변형 및 진동 검토
- 결과: 설계 검증 및 최적화된 블레이드 구조 확립
- 프로토타이핑 (Prototype Development)
- 목적: 실물 크기의 팬 모델을 제작하여 물리적 테스트 진행
- 주요 활동:
- 3D 프린팅 또는 CNC 밀링을 이용한 시제품 제작
- 조립성 및 기초 성능 테스트 수행
- 결과: 초기 프로토타입 완성 및 테스트 시작
- 성능 및 소음 최적화 (Performance & Noise Optimization)
- 목적: 최적의 냉각 성능과 소음 감소를 위한 설계 개선
- 주요 활동:
- 실제 환경에서 성능 검토 (공기 흐름, 소음, 진동 분석)
- 소음 최소화를 위한 설계 보완 (팬 블레이드 형상 및 모터 조정)
- 결과: 최적화된 팬 설계 및 프로토타입 수정 완료
- EVT (Engineering Validation Test)
- 목적: 제품의 주요 성능 지표를 검증
- 주요 활동:
- 냉각 성능, 공기 흐름, 소음 수준, 호환성 평가
- EVT 결과를 바탕으로 설계 수정 사항 도출
- 결과: 성능이 검증된 설계 확립
- TCE (열 크리프 평가)
- 목적: 팬이 고온에서 장시간 동작할 때의 성능 저하 여부 확인
- 주요 활동:
- 다양한 온도 조건에서 팬의 변형 및 성능 유지 테스트 수행
- 결과: 내열성이 검증된 구조 확립
- 사출 금형 개발 및 생산 최적화 (Injection Mold Development & Manufacturing)
- 목적: 대량 생산을 위한 금형 설계 및 제작
- 주요 활동:
- 사출 금형 설계 및 제작
- 사출 성형 매개변수(온도, 압력, 냉각 시간) 최적화
- 결과: 대량 생산 가능한 금형 완성 및 제조 최적화
- DVT (Design Validation Test)
- 목적: 최종 설계가 모든 사양을 충족하는지 검증
- 주요 활동:
- 냉각 성능, 소음, 전력 소비, 내구성 등을 테스트
- 결과: 설계가 최종 확정되어 대량 생산 가능 여부 확인
- LTCV (장기 열 크리프 검증)
- 목적: 장기간 사용 후 열로 인한 변형이나 성능 저하를 평가
- 주요 활동:
- 팬을 오랜 시간 고온에서 테스트하여 내구성 확인
- 결과: 장기간 사용 시에도 성능이 유지되는 것이 검증됨
- MVT (Manufacturing Validation Test)
- 목적: 대량 생산 공정이 품질 기준을 충족하는지 검증
- 주요 활동:
- 제조 공정에서 발생할 수 있는 문제 평가 및 수정
- 대량 생산 시 성능, 품질, 효율성 검토
- 결과: 대량 생산이 가능하도록 제조 공정 최적화 완료
- 최종 생산 및 품질 관리 (Final Production & Quality Assurance)
- 목적: 제품의 품질을 최종적으로 확인하고 대량 생산 개시
- 주요 활동:
- 대량 생산 전 최종 소규모 생산 진행 (Pilot Production)
- 제품 품질 검사 및 생산 효율성 분석
- 결과: 대량 생산 개시 및 시장 출시 준비 완료
이 개정된 PC 팬 개발 공정은 각 단계를 보다 명확하게 정리하고, 개발과 검증, 제조의 연계성을 강화하였다. 또한, FEM 해석 추가, 소음 최적화 과정 강조, 환경 내구성 평가 보완 등의 개선을 반영하여 실제 설계와 생산 과정에서 효율성을 극대화할 수 있도록 구성하였다.